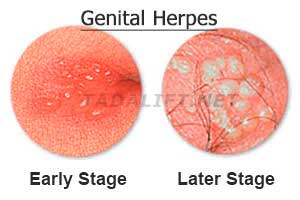
The data given by the WHO claims that 11% of the world’s population among the age of 15 and 49 are the carriers of genital herpes. Why the carriers? Because the virus (which herpes, actually, is) is incurable. However, it doesn’t mean that you’ll experience its symptoms permanently as the illness (but not the virus) can come and go away.
Ways of getting infected
One of the reasons why herpes is present in the blood of so many people is that it may easily be transitioned from the infected individual to his or her healthy partner. Usually, it takes about two to 14 days for the infection to show up. However, in most cases, weeks, months or even years can pass before you notice any signs of the disease.
It’s not difficult to catch genital herpes, especially when your sexual partner has sores on the skin or mucous membranes of the vagina. The common ways of receiving the virus are:
- Unprotected sexual activity including oral, vaginal, and anal sex;
- Shared usage of sex toys;
- Cuts on the skin;
- Touching the genitals affected by an outbreak of the ailment;
- From mother to an infant during labors.
Major threats of genital herpes
On the whole, the ailment doesn’t impose any danger to an adult person with a healthy immunity. However, having genital herpes, you risk to:
- Get an HIV infection. Sores on the skin make the penetration of the virus much easier;
- Get bacterial infection of herpetic sores;
- Pass the infection to a newborn baby;
- Have a miscarriage.
Ways of dealing with the herpetic viral infection
As we’ve already mentioned, genital herpes cannot be cured. However, there’s a good chance that you may have only a couple of outbreaks throughout your life. The bad news is that the weaker your immune system is, the more often you’ll have to face the issue.
To speed up the healing of the herpetic sores in the genital area, patients can use pills and ointments. Yet, as it may be difficult to reach the affected area, tablets are used more often. Among the three major genital herpes medications are valacyclovir, famciclovir, and acyclovir. Usually, the course of treatment lasts for a week or 10 days. Some people may need their therapy to be continued in case the sores are healing badly.
The frequency of genital herpes outbreaks may be lowered due to vitamin supplements intake, reduction of the stress levels, and strengthening the immune system on the whole.