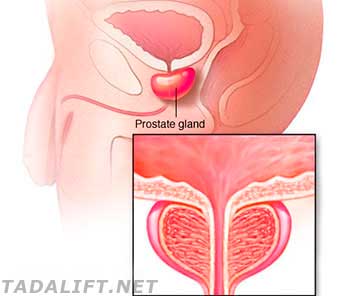
The first step to getting a clearer understanding of how the prostate affects male health is to learn its definition and basic functions. It surrounds the neck of men’s urethra and bladder and has the size of a walnut. This important hormone-producing organ is responsible for creating specific bodily fluids, and it’s essential to the healthy sexual functioning and regulating bladder control.
Important Role of the Prostate Gland
The prostate is necessary for men to reproduce, survive, and live comfortably, and that’s why different conditions that affect its normal functioning should be treated early. One of the main functions is the secretion of alkaline fluid important for semen, which is a mixture of the fluid produced by three sexual male glands, including the prostate. It plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system.
Other Basic Functions
This complex gland has a number of functions. The prostate also acts as a muscle that pumps the semen out of a penis with enough strength to help the sperm reach the cervix. It helps men with their sexual satisfaction by making sex desirable and helping procreation. The prostate is called the male G-spot because its stimulation usually produces a strong sexual response and intense orgasms in men. Besides, their ability to control ejaculation at this gland can result in a prolonged sexual intercourse.
The prostate gland is responsible for removing and filtering different toxins to protect the sperm and increase a change of impregnation. It also guarantees better sperm quality. Many doctors agree that it’s No. 1 function of the prostate. It also helps with healthy erections because it contains special nerves that trigger the penis to harden and swell.
In addition, prostatic secretions are important to protect the urethra from all kinds of urinary tract infections. The prostate acts as a valve, and it prevents the urine from leaving the bladder (unless it’s released by urination) and damaging the ejaculate during orgasms. It contains an important enzyme, 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for converting DHT. This potent hormone has many purposes in the male body, including male sexual functioning and drive.

