Dealing with the infection of the prostate (commonly known as prostatitis) may be not easy. Based on the form of the malady, you acquire, you may need different tactics of therapy. Furthermore, the urgency of your treatment and its duration will also depend on the type of the infection you’ve got. In general, there are three forms of prostatitis: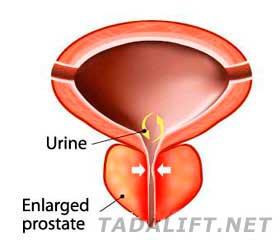
- Acute bacterial prostatitis;
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Let’s stop on each type of the ailment to know precisely what symptoms they commonly induce.
Acute form of bacterial prostatitis
Acute form of the malady develops very fast and needs immediate medical attention as it may grow into a life-threatening condition. To its main manifestations belong:
- Fever;
- Sickness and vomiting;
- Penile pain;
- Backache, lower abdominal pain;
- Troubles passing the urine;
- Pain and burning when peeing;
- Ache throughout the body.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
Speaking about the chronic form of the illness, it should be mentioned that it develops gradually. Its symptoms are mainly light to moderate. Because of this, the manifestations may be overlooked as they come and go. On the whole, the period of curing of this kind of prostate infection lasts for about three months.
The list of its common signs is as follows:
- Genital pain (in the penis, testes, scrotum);
- Need to pee too often;
- Urgent urination;
- Burning when passing the urine;
- Need to push to start peeing;
- Poor stream of the urine.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome
One of the most insidious forms of prostatitis is chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS). The bulk of its manifestations match those of the chronic bacterial prostatitis, but, in fact, the reasons and triggers of its appearance stay unclear as for now. The following list enumerates CP/CPPS major signs:
- Lower abdominal pain, back pain;
- Painful sensations in the pubis, which radiates to the penis and testicles;
- Extreme tiredness;
- Pain after ejaculation;
- Burning in the penis that doesn’t go away;
- Need to go to the bathroom too often;
- The urgency for urination.
A distinct feature of the disease is that it lasts for at least three months.

